About Us
we are dealing with solutions and spreading awareness among people and society regarding pollution
info@avinashtechy.com
+918171615141
Browse
Menu
An In-Depth Overview For the past few decades, environmental pollution in India has reached serious parameters with serious ramifications for human health, biodiversity, and the economy. With a rapidly growing population in the backdrop of industrialization and urbanization, India is fundamentally chained to several challenges ranging from serious air pollution to untreated sewage put in landfills. The article covers certain key types of environmental pollution in India, their causes and effects, and measures to combat these problems.
INDIA is a developing nation with over 1.4 billion people and has witnessed rapid economic growth and industrialization over the past decades. However, this growth of the economy has taken a huge toll on the environment. Environmental Pollution in the nation is a pressing issue affecting almost all aspects of life. From the very air we breathe to the very water we drink, pollution has become a ubiquitous problem in the country.
Environmental Pollution in India is caused by different sources, including industrial emissions, vehicle exhausts, agricultural runoff, improper disposal of waste, and deforestation. This has caused the degradation of air, water, and soil quality to truly alarming extents, threatening human health and sustainability.


The effects of air pollution include:
Important Data about India’s Air Pollution:

Water pollution is another serious environmental threat in India. Various human activities have considerably polluted India’s water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, and groundwater. The main modes of water pollution include the following
Consequences of Water Pollution:
Major Facts About Water Pollution in India:
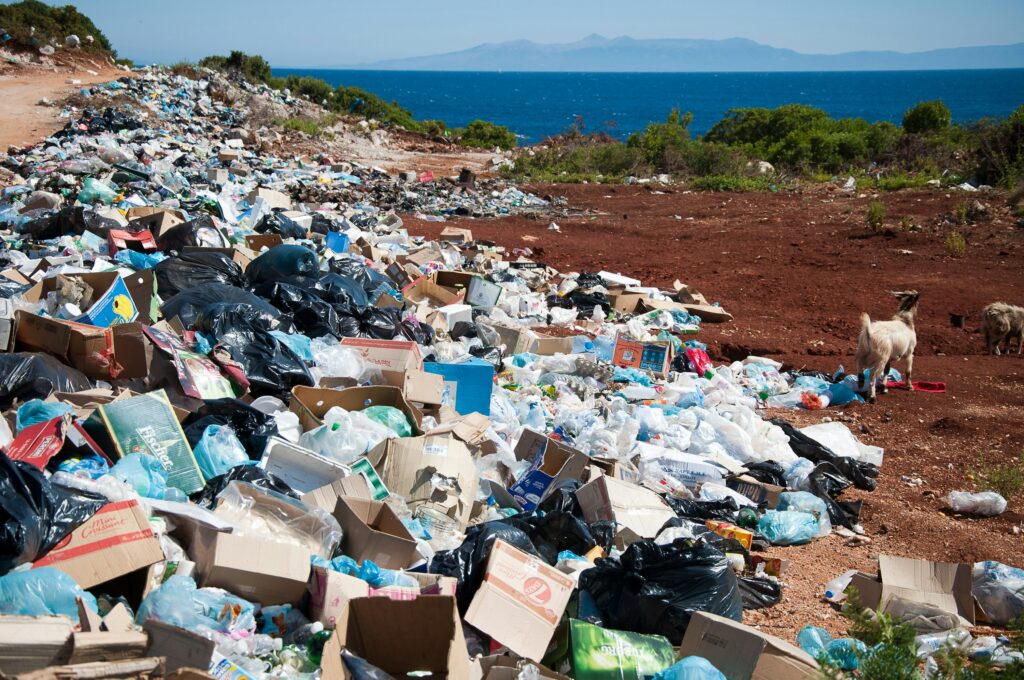

Soil pollution has turned into one of India’s major concerns, particularly in farming areas. The overapplication of chemical fertilizer, use of pesticides, and industrial waste has not only polluted the soil but has also made it highly toxic, impeding its fertility as well as the quality of food grown on it. The main causes of soil pollution in India include the following:
Consequences of Soil Pollution:
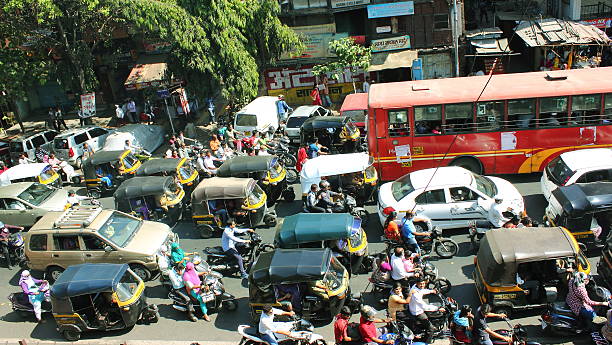
In India, noise pollution is a major issue that is often overlooked; it has serious repercussions on the environment and human health. The major sources of noise pollution are:
Effects of noise pollution include:
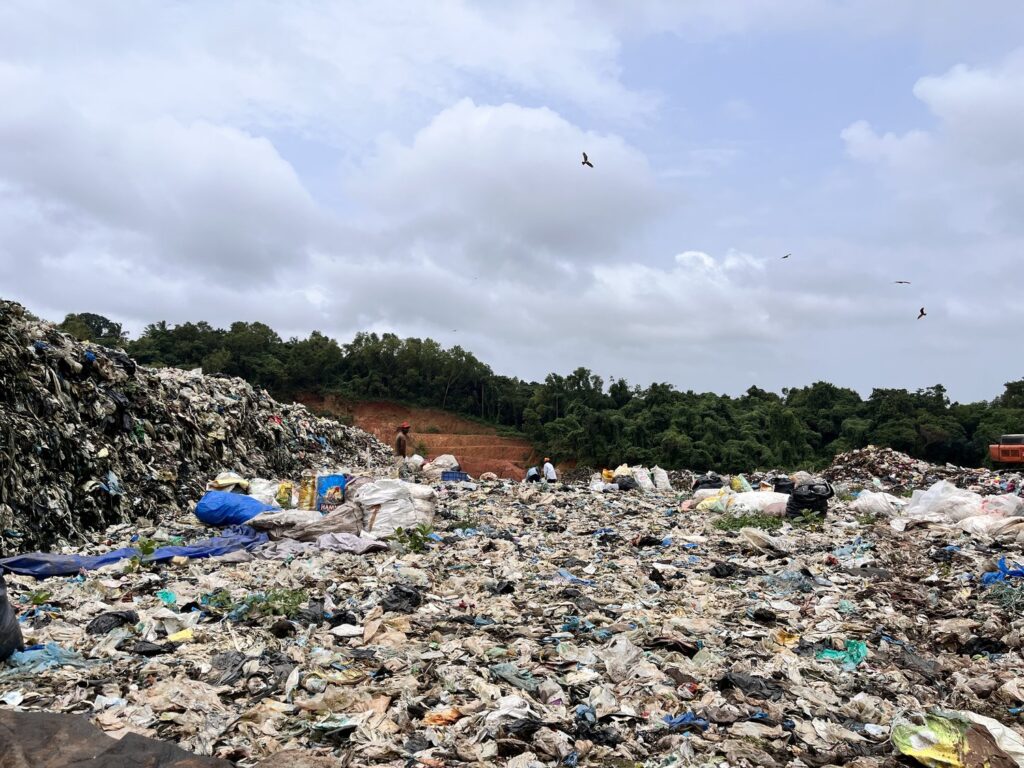

Plastic pollution in India is one of the most visible and, thus, dangerous forms of environmental pollution. The increased use of single- serve plastic products has caused massive destruction to the environment. Because of their non- biodegradable characteristics; that is, they remain in the environment for ancient times. The primary causes of plastic pollution in India are:
Consequences of Plastic Pollution:
which is harmful to marine life since plastic waste always ends up in oceans where it is ingested by marine animals.
all the way up to wildlife, including terrestrial animals that mistake plastic for food.

Garbage dumps and other hazardous materials generate land pollution in India because of improper disposal. Land pollution is brought on by improper waste disposal practices, disposal of industrial and domestic waste, and encroaching upon green areas. Other big causes include open dumping of waste.
Consequences of Land Pollution:
To remedy this environmental pollution, will take a combined effort by the locals with the help of the government. Following are suggested explanations, some of which are:
Promotion of Renewable Energy
Promotion of Renewable Energy Diversification into clean energy sources
The encouragement of renewable energies such as solar and wind power would reduce reliance on fossil fuels, which considerably contribute to pollution in the air. Supporting policies mechanism for greening technology: Businesses and economic actors should be stimulated toward the adoption of energy-efficient technologies, which will allow reducing some of the air pollution.
Promoting Public Transportation
Afforestation and Green Spaces
India’s air pollution is calling for serious attention owing to its effect on public health, wildlife, and the economy at large. But India can minimize pollution going to the future by putting in place very strict regulations, bringing in alternative sources of energy, improving waste management systems, and lifestyle orienting towards sustainability. This is the time when the government and the citizens should join as a team and take proactive measures on behalf of the environment for a safer dwelling for the future generations.
2-How many death are happening in india by pollution,on daily basis ?
In India, air pollution causes approximately 1.67 million deaths annually, which translates to about 4,500 deaths per day. The majority of these deaths are linked to diseases like heart conditions, strokes, and respiratory issues, all exacerbated by high levels of air pollution in urban areas.
3- How every person can reduce all type of pollution ?
Individuals can reduce pollution by using public transport, cycling, or walking instead of driving, reducing energy consumption, and adopting eco-friendly practices like recycling and reducing waste. Supporting renewable energy, planting trees, and using sustainable products also help. Small lifestyle changes collectively contribute to lowering pollution levels.
4 -According to WHO in which year pollution can be beaten ?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), pollution could be significantly reduced by 2030 if countries implement strict air quality standards and policies. This includes transitioning to cleaner energy sources, improving public transportation, and enforcing regulations on industrial emissions to reduce air pollution and its health impacts globally.
we are dealing with solutions and spreading awareness among people and society regarding pollution
info@avinashtechy.com
+918171615141